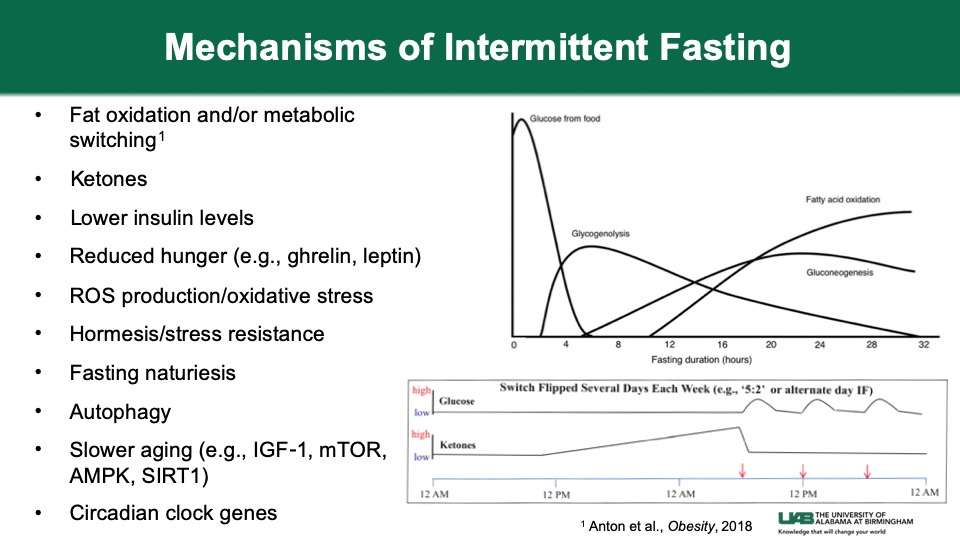
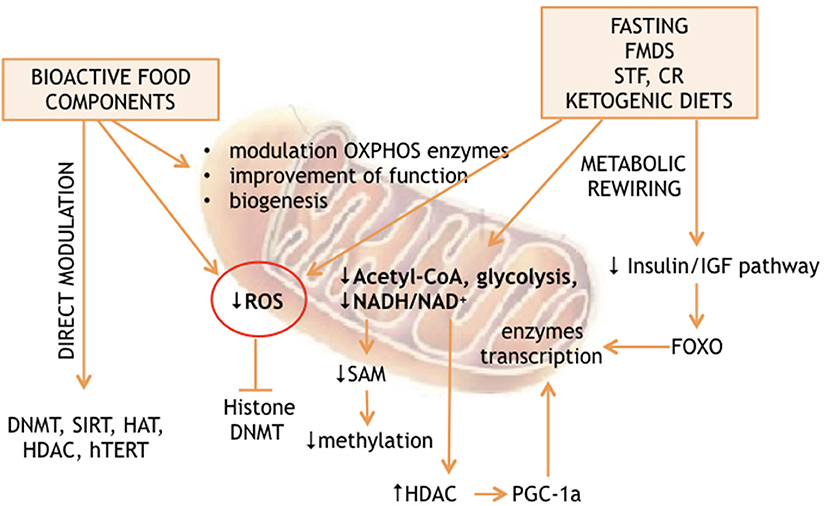
Many experience declining energy, slower recovery, and metabolic slowdown with age, even while maintaining healthy habits like exercise and nutrition. The root cause often lies not in lack of discipline or calories, but in mitochondrial dysfunction: damaged mitochondria fail to efficiently use energy from food, leading to fatigue, inflammation, insulin resistance, and reduced cognitive function.
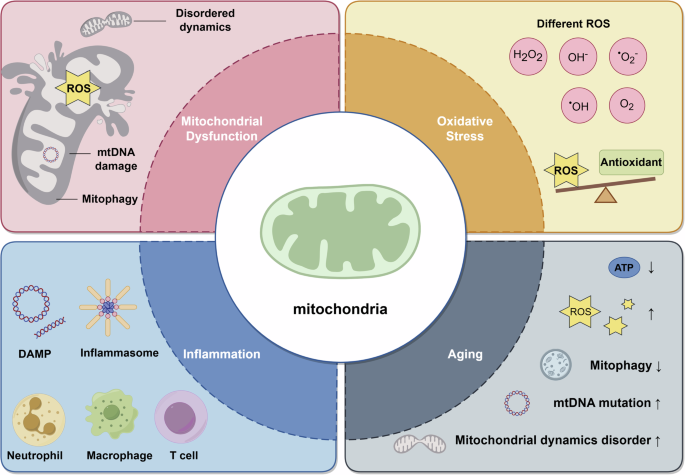
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Aging
As cells age, mitochondria become damaged, leak reactive oxygen species (ROS), produce ATP inefficiently, and accumulate instead of being recycled. This accumulation exacerbates energy loss and systemic issues.
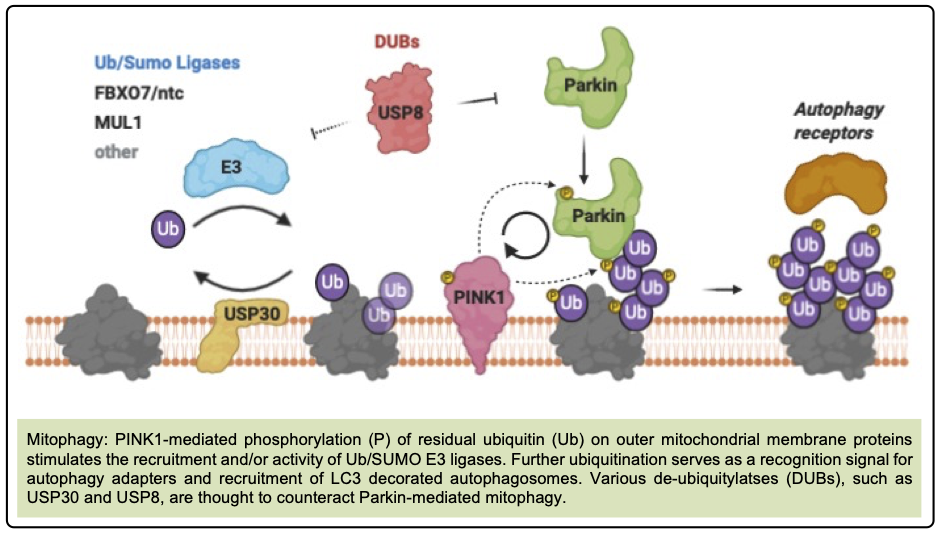
Mitophagy: The Cellular Cleanup System
Mitophagy is a targeted form of autophagy that recycles damaged mitochondria. It relies on proteins PINK1 (which accumulates on dysfunctional mitochondria) and Parkin (which tags them for degradation).
Spermidine enhances this process by promoting PINK1 accumulation and Parkin translocation, facilitating removal of damaged mitochondria and reducing oxidative stress.[1]
Spermidine’s Mechanisms
Spermidine, a natural polyamine, supports mitochondrial quality control rather than directly adding energy.
- It activates mitophagy for better cleanup.
- It inhibits the acetyltransferase EP300, reducing excessive protein acetylation in mitochondria. Over-acetylation impairs electron transport, lowers ATP output, and increases ROS; spermidine reverses this for cleaner, more efficient function.[2]
Link to Fasting and Longevity
Spermidine mediates many fasting benefits. In model organisms, blocking spermidine synthesis abolishes fasting-induced autophagy and lifespan extension; restoring it revives them. Spermidine amplifies caloric restriction pathways but does not fully replace fasting's broad effects.[3]
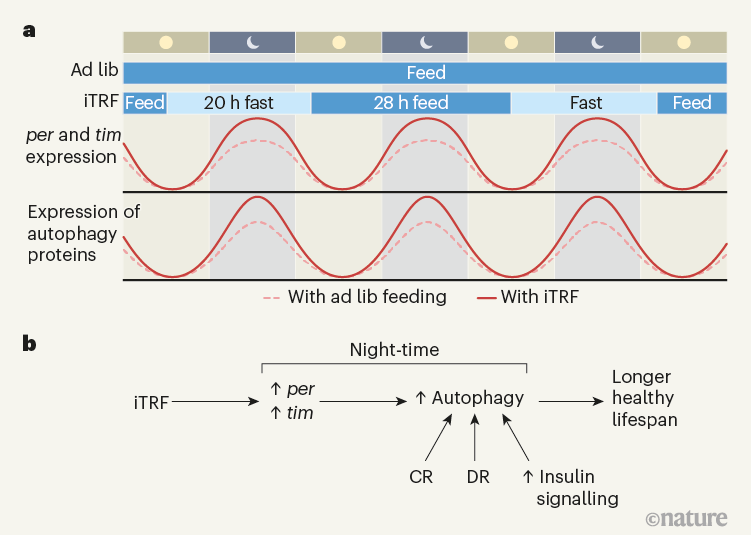
Timing with Circadian Rhythms
Autophagy and mitophagy follow circadian patterns, peaking in fasted states with low insulin and mTOR. Time-restricted eating aligned to earlier feeding windows enhances these; late-night eating suppresses them.
Taking spermidine toward the end of a fasting period (earlier in the day) optimizes mitochondrial renewal.
Rebuilding After Cleanup
Mitophagy clears damage, but new mitochondria require raw materials. Post-fasting refeeding with high-quality nutrients—particularly protein—supports mitochondrial biogenesis and stronger replacements. Cyclical patterns (clearance followed by nutrition) outperform constant restriction.
Practical Recommendations
- Focus on removing energy wasters through mitochondrial cleanup for sustainable vitality.
- Align spermidine and fasting signals with low-insulin periods earlier in the day.
- Use spermidine to support—not replace—time-restricted eating, exercise, and habits.
- Refeed adequately with protein-rich meals to rebuild mitochondria.
- Emphasize consistency: repeated small signals compound better than extremes.
- Build on foundational practices like balanced diet, movement, and sleep.
These mechanisms reveal how spermidine counters age-related decline by restoring mitochondrial efficiency.
References
[1] Qi Y, et al. ATM mediates spermidine-induced mitophagy via PINK1 and Parkin regulation in human fibroblasts. Scientific Reports. 2016. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep24700
[2] Pietrocola F, et al. Spermidine induces autophagy by inhibiting the acetyltransferase EP300. Cell Death & Differentiation. 2015. https://www.nature.com/articles/cdd2014215
[3] Hofer SJ, et al. Spermidine is essential for fasting-mediated autophagy and longevity. Nature Cell Biology. 2024. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41556-024-01468-x